If you plan to take the trail installation as it is to production, all you need to do is register the license. Click the Register link on the top right corner in the Web console, browse and select the license file that you received from us and get going.
If you are planning to move the trial onto a new server to host it in production, here are the steps you need to follow:
Note:
The procedure is same to move even your registered installation from server to another.
Again, the procedure is same for migrating from 32 bit to 64 bit OS and vice versa.
Fill in the form in the link given below:
https://www.manageengine.comservice-packs.html
After you register, your Annual Maintenance Support contract is validated and if your AMS is active, an email is sent to you with the service pack/upgrade pack link and the steps to apply the same. In case you don't have a valid AMS, you will be directed to our Sales team to renew the AMS, following which the service pack is provided.
The procedure to backup the OpManager database and restore it, is detailed in the User Guide here:
https://www.manageengine.comhelp/userguide/backup_restore.html
Few things to remember:
Backup during an upgrade
You need not restore the data in this case because the upgrade is on the same server and it is smooth. The data backup done here is just for disaster recovery, that is, assuming something goes wrong during the upgrade and the database breaks. You'll most likely not use this backup after the upgrade, because an upgrade might have introduced a database schema change, and the backed-up data cannot be restored on the upgraded instance.
Backup and restore between two different build numbers
As mentioned earlier, an upgrade can introduce a database schema change, though not always.. Let us assume you are on build 8723 and want to restore it on build 9011 on a new server. Following would be procedure:
If you encounter any errors during an upgrade or at start-up post upgrade, get in touch with opmanager-support@manageengine.com, with the relevant error message and a zip of the /opmanager/logs folder. The support team will assist you ASAP.
Click the Support-- About link found on the top right corner of the OpManager web-client to view your license information. You will also be able to view the latest build available on our website.
Steps to enable or disable SSL in OpManager:
For OpManager build 8050 and above.
This will enable the self signed SSL certificate for OpManager. OpManager webclient can be accessed in the same port number with https://
To Disable the SSL :
This will disable the self signed SSL certificate for OpManager. Hence the web-client can be accessed in the same port number with http://
For Builds older than 8050. (We have removed apache in build 8050)
Now you can try connecting to the web client with https i.e https://IPAddress:Port Number
Eg: https://192.168.223.23:80
Note: The above steps will work with OpManager build 7010 and above.
Attachments:
If you have installed NetFlow plug-in, then follow steps given below. These steps should be followed only if OpManger is SSL enabled.
The NetFlow plug-in will also be SSL-enabled now.
SNMPv3 is a user based security model. It provides secure access to the devices by a combination authenticating and encrypting packets over the network. The security features provided in SNMPv3 are Message integrity, Authentication and Encryption. If you select SNMPv3 as the credential type, then configure the following parameters.
Note: Only after configuring Authentication it is possible to configure Encryption.
Here are a few things that you can do to avert false postives:
OpManager lets you create powerful dashboards with over 90 widgets to choose from. The widgets display different fault and performance data with provision to drill-down. To know your network health at a glance, all you will need is a quick look at your favorite network management console , OpManager :)
We have had a few users asking us in our forums or writing to us at support to know if OpManager widgets can be embedded into their web pages. Yes, OpManager provides the flexibility of embedding widgets or dashboards into a web page, making it easier for a user or a group to access a specific set of information without having to log in and log out every time.
You can embed a widget or a dashboard using an <iframe>. For the benefit of those who have not seen the procedure posted in our forums, here are the steps:
Embedding a Widget
The code snippet to embed a widget is given below:
<iframe src="http://OpManagerServerName:Port/generateWidget.do?widgetID=194&widgetWidth=520" width=520 height=400 frameborder="1" scrolling="no">
In the above snippet, replace the src name with the actual host name and the port number on which OpManager is hosted and the ID of the widget that you want to embed. Mouse-over the edit icon on the top right corner of the widget to see the ID.
Embedding a Dashboard
You can embed the default dashboards or create a new dashboard and embed.
Here is the snippet to embed a dashboard:
<iframe src="http://OpManagerServerName:Port/customDashboard.do?methodCall=showCustomDashboard&dashboardID=303" width= height=in_pixelsin_pixels frameborder="1">
The snippet to access the dashboard without having to log-in every time is:
<iframe src="http://OpManagerServerName:Port/customDashboard.do?methodCall=showCustomDashboard&dashboardID=303&reqUserName=guest_user&reqPassword=guest_password" width=in_pixels height=in_pixels frameborder="1">
where the user name and password are passed as additional arguments.
Replace the user name, password and the dashboard ID. Access the required dashboard from the WebClient to see the ID passed in the url.
Note: DeviceName/IP header is a must for CSV file and other header fields are optional.
To discover devices from a selected range specify the start and end ip address and select the netmask for the devices to be discovered within that range.
To ignore VLAN interfaces,
Note: To disable Virtual LAN globally, try interface template.
If you want to administratively disable an interface, it is possible with OpManager in just a few clicks. Here are the steps:
The interface gets disabled and the interface's status is changed to Down. To enable the interface again, go to its snapshot page and click the Enable button under the Interface tab.
You can configure thresholds for multiple interfaces of the same type by editing the relevant interface templates.
OpManager purely relies on SNMP to represent the connectivity of nodes and links in the network.
1. Configure a seed device : A seed device is the core switch in your network. The switch must have SNMP-enabled so that OpManager is able to query the device and draw the links automatically, showing the connectivity of all the devices on your network. As changes happen to the networks frequently, OpManager allows you to configure an interval (in days) to re-draw the map. For instance, if a change happens once in a week, you can configure OpManager to re-draw the map every seven days.
The map is generated. You can change the layout by selecting the type as Radial Tree, Balloon Tree, Node Link or Custom option for the Layout combo-box on top of the network map. You can also export the map to Visio, or even save it as a business view in OpManager.
Prerequisites
Make sure you have Microsoft Visio 2007. Visio can be installed on any of your Windows devices and it need not be on the same server as OpManager. Ensure that you are able to access OpManager Weblcient from the machine where Visio is installed.
Installation
Exporting Views from OpManager
Loading the exported maps in Visio
To increase the size to say, 300 characters,
To change the timezone in OpManager,
For the all the devices by default OpManager sends one packet with time out as 1 sec. So if the WAN link stays busy, it is expected that OpManager will show that the devices on the other side as down. You can resolve this problem by increasing the ping time out, if needed even the packets sent to check the availability. However this facility will be common for all the device i.e. it is a global configuration.
Solution:
How to move OpManager from trial to production server?
Yet another frequently asked/discussed requirement is the ability to forward alarms in OpManager as traps to another trap destination. Requests are also raised to know if the incoming trap can be redirected to another application. YES, both are possible. Here is how you go about the forwarding:
Forwarding Traps
Here, OpManager simply forwards the SNMP Trap to another manager/device. Forwarding traps from OpManager involves a couple of configuration changes in two files. Refer the table below:
1. Effect the following configuration changes:
| File name & path | Existing entry | Modified entry |
|
/opmanager/conf/trap.forwarder |
 |
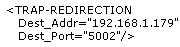 (replace with the correct IP address and port) |
| /opmanager/conf/trap.filters |  |
 |
2. Save the file and restart OpManager.
OpManager starts forwarding the incoming traps to the destination IP address and the Port mentioned in the trap.forwarder file.
Forwarding OpManager Alarms as Traps
You might want to forward the alarms in OpManager as traps to another destination/trap receiver. Here is how you do it:
1)Ensure Net-SNMP is installed on the OpManager server.
2)Create a batch file sendtrap.bat to invoke the snmptrap command. Place this file in /opmanager folder. The syntax for this command is as follows:
snmptrap options hostname community trap parameters...
For Version 1, the required trap parameters are:
where
| -v 1 | The SNMP version |
| -c | The community string and the default SNMP community string is public |
| %1 | The manager name, viz., the hostname or the IP address of the manager that must receive traps. |
| .1.3.6.7.2.1.3.1 | Specify the appropriate enterprise OID |
| %2 | The agent-name, that is the hostname or the IP address of the device for which an alarm is generated. |
| .1.3.6.7.2.1.3.1.1.2 | Replace with the appropriate specific OID |
| 1 | The generic type number |
| 6 | The specific type number |
| 10000 | The sysUptime in milli-seconds |
| s | Refers to the data type of the OID (string type) |
|
"%3,%4,%5,%6" (replace the % symbol with $ if you are doing it on a Linux box) |
The message from OpManager that can contain one or more of the following variables:
|
3)Configure a 'Run Program' notification profile specifying the following:
Command Name: sendtrap.bat
Program Arguments :[manager-name] $source $displayName $strModTime $category $severity $message
4) You can associate this notification profile to devices using the Quick Configuration Wizard. Whenever an alarm is generated on the managed devices, a trap is sent to the other monitoring server.
You can modify the IP Address to look at from the database, so that OpManager uses the secondary interface to monitor the service running on this interface alone.
Here is the procedure to do this.
1. Connect to mysql database using the following command:
cmd> cd [OpManagerHome]\\mysql\\bin
cmd> mysql.exe -u root -P 13306 OpManagerDB
2. Use the mysql update command to change the IP address to look at:
mysql> update InetService set TARGETADDRESS=1.2.3.4' where TARGETADDRESS='5.6.7.8';
1.2.3.4 is the secondary interface of the device
5.6.7.8 is the primary interface of the device. OpManager should have discovered the device through this interface.
And update the TARGETADDRESS only for the interface on which a particular service runs.
Try using the following command:
mysql> update InetService set TARGETADDRESS='1.2.3.4' where TARGETADDRESS='5.6.7.8' and NAME='machine-name-or-ip-address_ServiceName_Portnumber';
where machine-name-or-ip-address refers to the machine name or ip address of the device to be monitored ( it is mostly the primary interface in case of ip address)
ServiceName is the name of the service to be monitored which can one among Web, FTP, Telnet, MySQL etc.. as specified under Admin -> Service Monitors
Portnumber is the port on which the service runs like 80, 21, 23, 3306 etc...
To add a custom monitor for a resource of a particular device type, the device template must be modified. The new monitor should be defined in the device template so that the monitor is associated for all devices of that type. Here are the steps.
Applying the template to the other devices, adds the new custom monitors to all the selected devices, and the selected resources are monitored at the interval configured in the template.
Note: While selecting the WMI class, current value shown on mouse over is the raw data and it is NOT the value calculated using the appropriate counter type of the WMI performance counter.Upon associating to devices, counter values will be calculated based upon the counter types.
BY default these are the list of interface types( type number and name) which are considered as WAN interfaces inside OpManager.
18 DS1
20 Basic ISDN
21 Primary ISDN
22 Serial
23 PPP
32 Frame Relay DTE
33 RS-232
37 ATM
44 Frame Relay DCE
45 V35
49 AAL5
63 ISDN
64 V11
94 ADSL
96 SDSL
166 MPLS
To include any other type of Interface as a WAN interface to get SLA dashboard "WAN links by availability" report, we need to add the specific type into a table called "WANINTFTYPES"
For example to add an Ethernet/Fast Ethernet (which is of type 6) as a WAN interface, connect to the DB and run this query:
To connect to the Database (Mysql):
1) Open the command prompt
2) Go to the Mysql\bin directory and type the following
OpManager\mysql\bin>mysql -u root -P 13306 opmanagerdb
3) execute the following statement
4) mysql > insert into wanintftypes values(6);
5)exit
Stop and Start Opmanager and generate the report for Wan links. You can see all the Ethernet interfaces included in the report.
To receive alerts from the device, make sure you configure the routers to send traps to OpManager (you will not receive alerts from the device if the trap host is not configured in the source router). Telnet the router and type the following command:
snmp-server host (opmanager server IP) traps (host community string) rtr For instance, if the OpManager host IP Address is 192.168.18.128, and the community string is private, the command would be: snmp-server host 192.168.18.128 traps private rtr
You will mostly need this tab during evaluation to help you set up and configure the application to monitor your network. To remove the Intro tab in OpManager
1)connect to the DB bin:\>mysql.exe -u root -P 13306 OpmanagerDB (mysql.exe is under /opmanager/mysql/bin) 2)Execute this command. mysql>update panelprops set attribvalue='false' where nodeid='opmintro' and attribname='tab'; Now logout and login.
You will need to configure the VMware credentials for discovery before you actually proceed to discover. Here are the steps in detail:
You might also want to configure WMI credentials for the VMs if you want to add any custom WMI monitors or Windows service monitors etc..
After successful discovery, you will find the VMs and Host under the Virtual Devices category under Maps.
You can monitor only the required VMs on a Host. OpManager discovers all the VMs during the initial discovery and lists them under the inventory in the host snapshot page. Click on the relevant icon to monitor the required VMs on the host. OpManager maintains this configuration when a HA, VMotion, or rediscovery happens.
Pre-configuring a set of credentials in OpManager helps applying them to multiple devices at a time, saving a lot of manual effort.
1.Go to Admin --> Credential Settings
2.Click New in this screen
3.Configure the following parameters and click Add to add the credentials:
Using Quick Configuration Wizard
You can also use the Quick Configuration Wizard to associate a service to several devices at one go. Here are the steps:
Automatic discovery option is not available in the application as yet. Its a high priority item on our roadmap.
During initial discovery, OpManager categorizes the network devices into servers, printers, switches, routers and firewalls. The specifics for classifying devices based on type and category is defined in the device templates. Here are a few things that you need to do before adding the device, preferably in the same order so that the devices are classified properly based on type and category: 1. Add credentials 2. Enable the relevant protocols like SNMP, CLI or WMI on the monitored devices to enable manageability 3. Check and modify (or add new) device templates 4. Add the devices for discovery
Using the templates
You can check and modify the templates definition as follows:
You can also create a new template to acommodate a new device type as follows: Click ‘New Template’ to define a template for a new device type. Click the Template name to modify an existing one. Configure/Modify the following properties: Device Template: Specify the device type. Vendor Name: Select the vendor. Click Add New to add a new vendor, and Save. Category: Select the category for the device type. On discovery, the devices are automatically placed in the select Category map. Monitoring Interval: Configure the interval at which the device needs monitoring. Device Image: Select the image for this device type. System OID: Type the sysOID and click Add. Click Query Device for OpManager to query the device for the OID. Add Monitor: Click this option to select the monitors. Edit Thresholds: Click this option to edit thresholds. Click Create button to create the new device template. After adding or modifying the templates, add the device for discovery
Hyper-V devices are automatically discovered by OpManager and classified under the Virtual Devices map. Hyper-V is discovered in OpManager using WMI credentials.. So all you need to do is
Class A Network
The entire class A predominantly begins with 10.and is private, to be used in LANS When discovering Class A networks, do the following:
The Host Address Range for Class A Network: 10.0.0.1 – 10.255.255.254.
Class B Network
When discovering class B networks, the procedure is the same. Make sure you select the netmask as 255.255.0.0. The Host Address Range for Class B Network: 172.16.0.1 – 172.16.255.254
Class C Network
When discovering class C networks, the procedure is again the same. Make sure you select the netmask as 255.255.255.0.
OpManager relies on SNMP to get the interface details and its traffic statistics. Right now Opmanager uses RFC 1213 MIB and IF mib to get the port/interface details. So use mibbroswer.bat which is under /opmanager/bin and check if you are getting the VLAN port details by querying the Interface subtree in RFC 1213. Opmanager Should show the ports and the traffic if you get the response in mibbrowser. If it does, you will be able to add the traffic monitors and monitor them. To query the mib, follow the steps below: 1. Open the tool Mib Browser under Admin tab. 2. Enter the ip address of the monitored device in the host field with the correct community string. 3. Expand RFC 1213 mib as given RFC 1213 -> org -> dod -> internet -> mgmt -> mib-2 -> interfaces -> ifTable -> ifEntry Click ifDescr and click the Get button. Only this information is displayed in the UI of an SNMP enabled device.
Use the Mib Browser from the Admin tab or the MibBrowser.bat/sh utility in /opmanager home/bin folder to check the compliance. Select RFC1213 or RFC2096 from the dropdown and then select your device. RFC1213:
If the device does not support this OID, it will error out. RFC2096:
If the device does not support this OID, it will error out. If you do not see a MIB for RFC2096, you can download and upload it into OpManager. Google will provide a link to the MIB or check for its availability in http://oidview.com.
Service Packs and Hot Fixes are released from time to time and contain issue fixes, enhancements, changes, and new features.
1. Stop the OpManager server and make sure the Java.exe processes are not running in the task manager.
2. Take a backup of your existing OpManager installation by executing the BackupDB.bat in the OpManager\bin\backup
3. This creates a backup file in the OpManager\backup folder with the current date like for example 'BackUp_OCT10_2011_02_39_44_8812.zip' .Wait till the backup completes.
4. Once the backup process is complete, select Start --> Programs --> ManageEngine OpManager --> DB Manager --> DB Configuration.
5. A DB Configuration window pops up. Select MSSQL option and click OK. Configure the following information:
DB Host : The name or the IP address of the machine where MSSQL is installed.
Port: The port number in which OpManager must connect with the database. Default is 1433.
User Name and Password: The user name and password with which OpManager needs to connect to the database.It would be better if you could provide the "sa" user name and password as OpManager uses metadata, to create the tables.
6. These steps will automatically create the database in the MS-SQL.However the tables will be created only after successful start of OpManager. So Start OpManager with MS-SQL as the back end and shut it down after the successful startup.
7. Now run the RestoreDB.bat file under \OpManager\bin\backup folder on the ...\OpManager\bin\backup>RestoreDB.bat "D:\backup\BackUp_OCT10_2011_02_39_44_8812.zip"
8. Once the restoration is complete, start OpManager. This should restore the data in MS-SQL database.
You can bulk-configure interface monitoring parameters by editing the interface templates.
The configuration change is applied to all the interfaces of the same type.
Prerequisites:
Must be pingable
Must have SNMP enabled
Before you add, quickly run this check:
Check 1
Check 2
Proceed
Now, add the router for discovery. It will be properly classified and monitored.
The SNMP OID that returns temperature on Cisco devices is .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.13.1.3.1.3.1. Not all catalyst devices support this. This variable is implemented in CISCO-ENVMON-MIB. Load the mib in the MibBrowser and check if the device responds to a query to this variable.
OpManager shows the connectivity between a switch and other connected devices in the network in Switch Port Mapper. You get the details such as the MAC address, IP Address and DNS names of the devices connected to the switch. You need to provide the details such as the community string and port number of the switch and if needed, the details of the server or router that may contain the layer 3 details. To view the switch port mapping details, follow the steps given below:
This should be possible with Syslog monitoring.
https://www.manageengine.comsyslog-monitoring.html
https://www.manageengine.comhelp/userguide/add_syslog_rules.html
The other option is to configure the router or switch to send a trap notification whenever a login occurs.
To configure a new alarm escalation rule, follow the steps given below:
This option to suppress alarms is useful in cases where the devices are under maintenance or if there are some 'known' hardware or software issues on the systems. Suppressing alerts is one way to avert false alerts. Configuring Alarm Suppression for a Single Device
Alarms of this device will be suppressed for the selected period Configuring Alarm Suppression for Multiple Devices
OpManager is available in English, Spanish, Chinese Simplified, Chinese Traditional, Japanese, French, German, and Italian languages and it can be selected during installation. Below are the steps to change OpManager from one language to other supported language(English to Spanish).
1. By default the language will be set for English.
2. All supported Languages directory is maintained under OpManager\ancillary directory.
3. copy the serverparameters.conf from the respective language directory, for ex : Spanish \OpManager\ancillary\sp\html and replace them under OpManager\conf\ .
cn - Chinese [chinese simplified]
de - German
en - English
fr - French
it - Italian
jp - Japanese
sp - Spanish
tw - Taiwanese [chinese traditional]
kr - Korean
Restart OpManager.
OpManager identifies the Windows server as a DomainController during the initial SNMP-based discovery. Based on the SNMP response, it automatically classifies the device under the Domain Controller category and is grouped under the map of the same category. Upon classification as a DC, the DC gets added with the AD dashboard. If it has correct WMI credentials, all the AD dashboard monitors will automatically populate the values. In your case, since the device is already discovered, enter the correct WMI credential and manually change the category to Domain Controller.
OpManager processes traps from devices into meaningful alerts.
Though the trap OID is the same, there must be some difference in the varbinds which shows the AP's names. OpManager can process that value (failure component) and create a new alarm for each Access Point. Refer to the following link for steps to know about trap processing in OManager.
https://www.manageengine.comhelp/userguide/processing_traps.html
Open a CLI session on the destination router and enable the EXEC mode as follows:
Router>enable
Start the global configuration mode:
Router#configure terminal
Enable the IP SLA responder:
Router(config)#ip sla responder
[or] Router(config)#ip sla monitor responder
(Note: Enter any one of the command to enable IP SLA responder as it varies according to the IOS versions.)
Repeat the above steps for all the destination routers on which you want to monitor VoIP performance.
Make sure you discover the router in OpManager and configure the SNMP read and write community. And then, add the monitor as follows:
The data is collected every hour, from the time you have configured.
Define a template with the required VoIP settings to be used for monitoring performance. The VoIP template comes with pre-populated default values. Incase you would like to effect some changes to the values before initiating monitoring, make the changes as follows:
Defining Thresholds for the monitored parameters: You can define a threshold template so that the VoIP performance parameters can be better suit your company SLA's (Service Level Agreements). Alerts are triggered based on the thresholds configured so that you can take corrective actions in time. Here are the steps to define a threshold template:
OpManager primarily relies on Cisco's IP-SLA for monitoring the VoIP and the prerequisite therefore is, that the device should be a Cisco Router and must have IPSLA agent enabled on it. From IOS Version 12.3(14)T all Cisco routers support monitoring of VoIP QoS metrics. Cisco's IPSLA, an active monitoring feature of Cisco IOS software, facilitates simulating and measuring the above mentioned parameters to ensure that your SLAs are met. Cisco IP SLA provides a UDP jitter operation where UDP packets are sent from the source device to a destination device. This simulated traffic is used to determine the jitter, the round-trip-time, packet loss and latency. This data is gathered for multiple tests over a specified period to identify how the network performs at different times in a day or over a few days. The VoIP monitor gathers useful data that helps determine the performance of your VoIP network, equipping you with the required information to perform network performance assessment, troubleshooting, and continuous health monitoring.

In VoIP Monitor, business views help you to know the status of the device and call path between devices at a glance. Whenever a new VoIP monitor is created, a business view (image shown below) of it also gets created automatically with the default background and device icons. However, later you can modify the background and device iconsif required.

In the business view, mouse-over the device icon or name/IP and call path to view its details. Click on the device icon or call path will open the snapshot page of the device or the call path respectively.
Accessing VoIP Monitor Business Views
If the time on OpManager is different from the Server time, follow the steps given below to fix the issue:
1. Save the attached file and rename it to time.jar and place it under \OpManager folder.
2. Open a command prompt and go to \OpManager folder and execute the command below by providing your exact time zone difference from the GMT.
cmd:/> jre\bin\java -Duser.timezone=GMT-9:00 -cp time.jar Time
Modify the query according to the time zone difference in your region. Here I am executing the query for changing the OpManager time to Alaska Time zone which is GMT -9.
3. Take a back up of wrapper.conf located under \OpManager\conf folder.
4. Open the wrapper.conf and search for Java Additional Parameters and at the end of the additional parameters, add the entry below.
wrapper.java.additional.12=-Duser.timezone=GMT-9:00
After modifying it, the changes will look as below.
# Java Additional Parameters wrapper.java.additional.1=-Dcatalina.home=apache/tomcat wrapper.java.additional.2=-Dmysql.home=mysql #wrapper.java.additional.3=-Dwebserver.port=80 #wrapper.java.additional.4=-Dresource_check="80,8009" wrapper.java.additional.3=-Djava.library.path=lib wrapper.java.additional.4=-Dwebserver.rootdir=apache wrapper.java.additional.5=-Djava.rmi.server.codebase=apache/tomcat/conf/workers.properties wrapper.java.additional.6=-Dcom.adventnet.me.opmanager.showprogress=true wrapper.java.additional.7=-Dcom.adventnet.me.opmanager.service=true wrapper.java.additional.12=-Duser.timezone=GMT-9:00
5. Save it and start OpManager as a service which will fix the problem.
Note: 1. The above changes will be in effect only if OpManager is started as a Service.
2. "wrapper.java.additional.12=-Duser.timezone=GMT-9:00" - This line needs to be place at the end of the file and also change the line number(eg: 12) accordingly.
Steps to correct the time difference issue in OpManager-NFA plugin
1. Goto OpManager\Netflow\bin folder and edit the "run.bat" in a text editor and search for the following line:
set JAVA_OPTS=%JAVA_OPTS% -Dprogram.name=%PROGNAME% -Djboss.server.type=com.adventnet.j2ee.deployment.system.AdventNetServerImpl
Change the above line as follows:
set JAVA_OPTS=%JAVA_OPTS% -Dprogram.name=%PROGNAME% -Duser.timezone=GMT-9:00 -Djboss.server.type=com.adventnet.j2ee.deployment.system.AdventNetServerImpl
2. Restart OpManager service and the Netflow module would show the correct time. Note:GMT-9:00 timezone is shown as an example.Please modify it as per your timezone.
Attachment: time.jar 606 B
From Home --> Dashboards -->, click on New Dashboard. Create New Dashboard window opens. Configure the following details.
The default dashboards in OpManager cannot deleted. You can delete the custom dashboards. Here are the steps:
To add a new widget to a dashboard follow the steps given below:
To delete or edit a widget,
Many users get confused with 'sysuptime' from RFC1213 MIB, but it is not representative of the system uptime. It is the time in hundredths of a second since the network management portion of the system was last re-initialized.
You have to use hrsystemuptime to find the system uptime. You can add this as a new monitor to the existing device templates through Add Monitor -> Add Bulk option. [ Use the add bulk option to include mathematical expressions to the monitor ].
hrsystemuptime OID is ".1.3.6.1.2.1.25.1.1.0". You have to divide this by 8640000 to give the system uptime in days.
See the attached image to findout the expression to be used and the value that i got from this OID for an SNMP node.
To this, you can configure thresholds.
To monitor the folder on both local or remote server you should specify the path as follows: Drive:\FolderName ( Example C:\FolderName )and you can view our File & Folder monitor
More details in the User Guide:
File monitor https://www.manageengine.comhelp/userguide/file_monitoring_template.html
Folder monitor https://www.manageengine.comhelp/userguide/folder_monitoring_template.html
We have seen what are unknown devices. Let us see what you need to do to resolve the problem.
To reduce the number of devices getting classified as 'Unknown', configure the correct credentials even before initiating discovery. Doing this saves a lot of time and effort on re-work.
Resolving Unknown devices in the devices already discovered
SNMP-enabled devices
If the device supports SNMP, enable SNMP and rediscover the device. Despite this, if you face issues, troubleshoot as follows:
Similarly, for switches and printers too, enable SNMP in the device and rediscover.
CLI / WMI-enabled devices
If you have decided to disable SNMP authentication on Unix-based servers, configure Telnet or SSH credentials and associate the credentials to the servers. Similarly, for Windows devices, configure WMI credentials and associate the credentials to the devices. Re-discover the devices with the new credential
To create a custom dial graph, please follow the below steps. Lets take your scenario, where you want to point the custom monitor to the dial graph for a Firewall device. Here are the steps.
1. Open the file opmanager_snapshot_dial.xml and scroll to Firewall section.
2. Add PARAM type and pollKey for each dial names. where, PARAM type is the device type. eg: Juniper pollKey is the custom monitor name. eg: JuniperCPU Similarly you can do this for other device types like Servers, etc.. Replacing the custom monitor to the Pollkey can point the monitor value to the dial graph
3. I have added a custom monitor called JuniperCPU.
For eg:
<CATEGORY name="Firewall"> <DIAL name="CPUUtilization" displayName="webclient.devices.details.cpu" dialType="meter" shortKey="CPU"> <PARAM type="sonicwall" pollKey="CPUUtilization"/> <PARAM type="Juniper" pollKey="JuniperCPU"/> <PARAM type="Fortigate" pollKey="FortigateFirewallCPUUtilization"/> <PARAM type="Netscreen" pollKey="NetscreenFirewallCPUUtilization"/> <PARAM type="Cisco PIX" pollKey="CiscoFirewallCPUUtilization"/> <DEFAULT pollKey="CPUUtilization"/> Similarly, you can add the entries for DISK and Count Utilization.
4. Save the file and Restart OpManager to take effect.
Note: Backup opmanager_snapshot_dial.xml before modifying. Similarly you can associate custom monitor for other categories like Server,Routers etc.
OpManager supports DNS environment. If the device is added with DNS name, all the queries will be sent only to the name and not IP. We can configure OpManager to poll only by name and not by IP address. Open serverparameters.conf under /OpManager/conf in a wordpad and find this entry PING_USING_IPADDRESS true change it to PING_USING_IPADDRESS false
Restart OpManager. Try adding one such device using Admin-->add device(use DNS name).
The Snmpv3 communication between two SNMP Entity starts with handshake process. This process contains two steps, first one is Discovery and second one is TimeSynchronization process. And for snmpv3 communication, the manager needs to know the agent's details inorder to communicate with the agent.
1. SnmpEngineTime.
2. SnmpEngineBoot.
3. SnmpEngine ID.
As per standard, the above information is retrieved from the Cisco router by using Discovery and TimeSynchronization process.
The net-snmp will accomplish both discovery and timesync process in a single request instead of two requests as the discovery response itself contains EngineTime, EngineBoot and EngineID. This behavior is implemented in our SNMP layer and will be rolled out in our next release. However, as per RFC3414, Cisco device should respond for discovery and timesync requests.
For your clear understanding, the discovery & timesync process is explained below:
Discovery Process:- First the Manager (OpManager) sends a discovery packet to the Agent to get the Agent's Authoritative EngineID value. For further communication, this EngineID value is used. As per RFC3414, the Discovery PDU packet is issued with following parameters:
i) EngineID value as zero length
ii) Security level is noAuthNoPriv
iii) UserName may be zero length or dummy userName.
For this request, the Agent responds with EngineID and UknownEngineID counter value. Instead of empty string, we use the userName as "initial". I would like to clarify that why RFC is recommend to use the userName is empty string, for discovery process is as follows Refer RFC3414 [Page 16] - The msgUserName specifies the user (principal) on whose behalf the message is being exchanged. Note that a zero-length userName will not match any user, but it can be used for snmpEngineID discovery. The reason is that the UserName of the request PDU is not matched with configured user details in the SNMP Entity (agent) while processing the Message. As per RFC3414, the processing of SNMP packet is as follows:
i) First, the SNMP Header field is decoded
ii) SecurityParameters fields are extracted from the Packet. First Authoritative EngineID value is extracted from the packet. If the EngineID is zero length, agent takes this request as Discovery and it responds with EngineID value with usmStatsUnknownEngineIDs counter value
iii) Refer the RFC3414 [Page 25] Processing an Incoming SNMP Message. b) the usmStatsUnknownEngineIDs counter is incremented, and an error indication (unknownEngineID) together with the OID and value of the incremented counter is returned to the calling module. Note in the event that a zero-length, or other illegally sized msgAuthoritativeEngineID is received, b) should be chosen to facilitate engineID discovery. Otherwise the choice between a) and b) is an implementation issue. The SNMP request packet is sent with zero length engineID value, so the cisco device(agent) should properly respond for this request irrespective of whether or not the userName is initial or empty string. It is a good practice to send with empty string. This is already implemented in our SNMP library.
TimeSynchronization Process:
The time synchronization packet is issued with given username and securitylevel as Auth_Priv. The agent responds with enginetime and engineboot and with USMStatsNotInTimewindow conter value. Note that the UserName from the second packet onwards, configured userName whose behalf the request to be issued will be set in the request packet. In this process, the authentication i.e authProtocol/ authPassword are verified.
Here is what you need to do to resolve the issue. You will find a print to the following effect in the logs: Caused by: java.sql.SQLException: The transaction log for database 'OpManagerDB' is full. To find out why space in the log cannot be reused, see the log_reuse_wait_desc column in sys.databases..
To check the used %: DBCC SQLPERF(LOGSPACE) Steps to clear the logs.
1. Shutdown opmanager server
2. Change the Recovery Model to Simple by following the steps below:
Go to SQL server-->OpManagerDB properties-->Options-->Recovery Model-->Simple.
3. Connect to MSSQL Server-->OpManagerDB. Execute the following query
1) DBCC SHRINKDATABASE (database name , target percent) for eg DBCC SHRINKDATABASE (opmanagerdb,20)
2) alter database <DATABASENAME > MODIFY FILE (Name = "<DATABASENAME>_log",MAXSIZE=1 GB) - for eg alter database opmanagerdb MODIFY FILE (Name = "opmanagerdb_log",MAXSIZE=1 GB) (If the transaction log is too huge without any backup, it can not be shrinked. So run this query and then follow the above steps
BACKUP LOG OpManagerDB WITH TRUNCATE_ONLY
4. Restart OpManager Server.
Ensure you upgrade to the latest build.
You just need to tell OpManager which paths you want to monitor i.e source and target. The source router(Cisco router enabled with IPSLA agent) should be discovered by the OpManager. For example: If you want to monitor latency and availability of branch office from your main office, you need to have a Cisco router enabled with IP SLA agent in your main office and this router should be discovered in the OpManager.
Refresh the page after few seconds and go to all monitors page to see the new monitor. The data will be collected every 5 minutes , from the time you have configured.
When you configure a WAN RTT monitor, OpManager starts collecting data every 5 minutes. At each poll, if the latency and availability threshold values are violated, OpManager triggers an alarm. After 5 minutes, if the latency threshold of the monitor is violated, an alarm is listed in the WAN RTT Monitors dashboard.
OpManager does not support SNMP V3 for WANRTT yet.
We have plans to use only the read community for WANRTT configuration (Import option for the existing monitors using read community which is also under development phase). OpManager uses SNMP write to configure IPSLA (WAN RTT)settings in the source router. Though it is similar to "Write" command, some models(IOS versions) do not work with this. So once you configure a new WAN RTT monitor, login to the source router and run "write" (or equivalent command in new versions).
These modules are license based. Even the professional edition has free monitors for VOIP and WAN RTT and is therefore not removable as of now. We will make this customizable in future.
You need to configure the WAN RTT Monitors separately and add it to the existing / global business view as a shortcut. The steps are explained below:
Refer the screenshot below, with two WAN endpoints added- "Site1" and "Site2" to the existing WAN RTT monitor business view:
Repeat the same when you want to add new monitors to the existing view. Now you can see all the new wan end points in the same business view.

You can use our WAN RTT Monitor add-on to monitor the latency of end routers.
We use Cisco IP SLA to monitor the latency and raise alerts based on the thresholds you configure in OpManager. To know more about Cisco IP SLA, look at the link given below: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/ipsla/configuration/guide/ The WAN RTT (Round Trip Time) Monitor will help you,
a) Monitor latency between end points across WAN
b) Raise alerts based on the Round Trip Time thresholds. The thresholds are customizable.
c) Monitor Latency for each HOP between the end points.
d) Custom reports to identify the problem quickly.
e) Auto-Configuration of Cisco IP SLA monitors to the router, without having you to log on to the router.
Download the SQL Native Client from the link below. You will need to scroll down the page for the Native Client downloads:
http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?id=16978
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 Native Client (SQL Server Native Client) is a single dynamic-link library (DLL) containing both the SQL OLE DB provider and SQL ODBC driver. It contains run-time support for applications using native-code APIs (ODBC, OLE DB and ADO) to connect to Microsoft SQL Server 2000, 2005, or 2008. SQL Server Native Client should be used to create new applications or enhance existing applications that need to take advantage of new SQL Server 2008 R2 features. This redistributable installer for SQL Server Native Client installs the client components needed during run time to take advantage of new SQL Server 2008 R2 features, and optionally installs the header files needed to develop an application that uses the SQL Server Native Client API.
X86 Package (sqlncli.msi) X64 Package (sqlncli.msi) IA64 Package (sqlncli.msi)
For more details on installing the native client, refer this site: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms131321.aspx
Courtesy: http://msdn.microsoft.com
Here is a quick video guide on installing the sql native client:
Note:
1. OpManager 9 & below version users- Ensure that the files bcp.exe and bcp.rll are present under
OpManager 10 version users - Ensure that these files are present under
You will find these files in MSSQL installation setup.
2. If the MSSQL server is installated on a 64-bit OS, and OpManager Central is installed on 32-bit server, the bcp.exe and bcp.rll copied from the MSSQL server will not work on the OpManager machine. You'll need a 32-bit bcp.exe and bcp.rll.
Make sure the right monitor is added for the server. Either WMI or SNMP, you have these set of monitors.
You can set thresholds for all the monitors and get the alert once it is violated.
Follow the steps detailed on the following page in the VMware website:
http://pubs.vmware.com/vsphere-4-esxi-installable-vcenter
Follow the detailed instructions provided in the link below:
http://www.vmware.com/pdf/vsp_4_snmp_config.pdf
Intructions to enable SNMP on ESXi 4.1 using remote CLI are available in the link below:
http://www.fatmin.com/2010/08/enabling-snmp-in-esxi-41-using-the-remote-cli.html
If the customer has installed OpManager on Linux without being aware of the WMI limitations on linux or any other reasons and wants to move it to a Windows machine, follow the steps below.
Now check if everything is fine and WMI is also working properly. If you face any issue in between, please call support immediately.
As per the design OpManager triggers 3 alarms for the device down state - when it misses 1 poll (attention), 3 poll (trouble) or 5 poll (critical). It sends only one email notification based upon the option selected for when the Device misses poll(s) in the Notification Profile.
The following are the possible reasons for the multiple email notification,
a) Admin --> Alarm Escalation - Check whether you have enabled any Alarm Escalation for the device.
b) Notification Profile - Check whether you have enabled when the Device misses poll(s) on multiple notification profile and associated the device.
You can use either of the below way to do it,
1 You can quickly suppress the alarms for a period of time to not receive alarms or alerts during that period: Admin --Quick Configuration Wizard -- Associate an Alarm Suppression rule to several devices -- Select the time period -- Associate the rule to the required devices.
2. Create a Down Time Schedulers for the devices during the actual downtime,
Admin -- Down Time Scheduler
Refer for more information :
Here are the steps to make OpManager send alarms when data is not collected:
There is a limitation of configuring negative values in Add Bulk Option at the moment. You can work around by first creating the monitors using the Add bulk option without configuring the threshold value. Then edit the monitor separately and configure thresholds for the same. This will work fine. Will keep you posted on the feature implementation.
The import/export template option is useful when you want to share a custom template you created with the community or import a template from the community.
Exporting templates:
If you want to share it with the community, for now, you can post it on our forums, or email it to us. You can also upload it via this form.
Importing templates:
To associate the templates,
OpManager can be configured to send 'Data not collected' alerts when monitoring and data collections stops for some reason. This requires a little tweak to a configuration file. Here are the steps:
'Data not collected' alarms is now generated when data collection fails for some reason.
There should be a Security Event generated when that AD account logs in. We can create an EventLog rule and in the match string, give the account name for the exact filter. Do check this link.
https://www.manageengine.comhowto_demos/eventlog_monitor/demo1.html
OpManager uses Windows NTFS compression. Folder attributes will be changed and the font colour will become blue.
http://www.microsoft.com/resources/documentation/windows/xp/
If you are monitoring the localhost, that is the system where OpManager is running, then you need to leave the WMI username and password blank.
You can associate a Windows service monitor or a TCP service monitor to several devices using the quick configuration wizard.
Repeat process to associate other services to multiple servers.
Go to the device snap-shot page --> Notification Profile --> Edit the profile and choose- when the Device misses 5 poll(s) (select 3 or 5).
For ex : If you have set the polling interval for the device as 5 min then you can select 3 and if 3 minutes, you can select 5. Modify the polling interval accordingly so that it polls for 15 min and then alerts.
To effect the changes for bulk devices:
Go to List View page---> Select the required devices --> Click on More --> Monitoring Interval and specify the interval.
OpManager script monitoring provides a lot of flexibility to achieve some network monitoring tasks which is otherwise not available in a solution out-of-the-box, or even with integrated solutions.
Usecase
This usecase demonstrates how OpManager uses Script monitors to find the sum of the values of two monitors on a monitored database server and alerts if the collective size exceeds a certain threshold. The monitor by default returns multiple instances (SQL instances on a DB server), and this usecase derives a sum of the size of two specific instances. You can extend the same procedure to perform several other tasks my querying a database (in this example, the opmanager database) through a script.
Prerequisites
MySQL .Net connector: http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/net
The custom script
Attachment: ![]() CPU Util Sum.xml
CPU Util Sum.xml
Here is the video capture leading you through a step-by-step configuration:
If you are unable to view the embed above, visit this link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0BB4uvc8i1k
Go to Support link on the top right corner of the OpManager GUI. Click Support -- Support Information File to create the file. Once the file is created, a message with a link to the file, is displayed. Send that file to support for analysis.
Go to the device template in which the new custom monitor was added.
Click Add monitors-->Scroll down to the bottom to find custom monitors. You will also find an option to delete the monitor at the right hand side.
The powered off VM needs to be configured for alarm suppression to disable any further alarms. To configure alarm suppression, follow the mentioned action in OpManager : VM snapshot -- Actions -- Suppress Alarms, or Admin -- Quick Configuration Wizard -- Associate an Alarm Suppression rule to several devices.
The DHCP scope monitoring OIDs are present in the DHCP mib.Hence the following DHCP mib and MSFT mib has to be placed in the OpManager\mibs folder.Find them attached in this KB article.
The OIDs are .1.3.6.1.4.1.311.1.3.2.1.1.3 for FREE IPs and .1.3.6.1.4.1.311.1.3.2.1.1.2 for IN USE IPs in a network address
Verifying the OIDs
Run the mibbrowser.bat in the OpManager\bin folder and load the DHCP mib.
Fill the details of the HOST,community with the details of the DHCP server
Paste the OID for FREE IPs in the ObjectID field and click on Operations -> Get
If you get the output of the FREE IPs available in every network in the DHCP pool,create custom SNMP monitors using the procedure in the how-to link below
https://www.manageengine.comcustom-SNMP-monitors.htm
As you can see the OIDs above are numeric as well as tabular hence they give output for multiple networks in every poll.
Updating changes in Database
Once you have created the SNMP monitors (Free IPs and IN USE IPs) in the Windows template and applied it to servers,type the following in the browser
http://OpManager server:port/SubmitQuery.do
Paste and run the following query after inputting the DHCP server name and DHCP monitor name.
update polleddata set saveabsolutes='true' where name like '%DHCP monitor name%' and agent like '%DHCP server name%'
For example :
update polleddata set saveabsolutes='true' where name like '%DHCP FREE IPs%' and agent like '%fscvopdhcp01%'
Repeat the same procedure for DHCP IN USE IPs monitor as well.
Note: Please make sure you backup OpManager before running the above query.
Attached Files :
DHCP Scope monitor.png 85.85 KB
If you have any questions about OpManager, feel free to raise a support request and we’ll get back to you.
